The key difference between glycosidic bond and peptide bond is that glycosidic bond are involved in the linkage of carbohydrate molecules while peptide bond are responsible for connecting amino acids in proteins.
What is the Glycosidic bond?
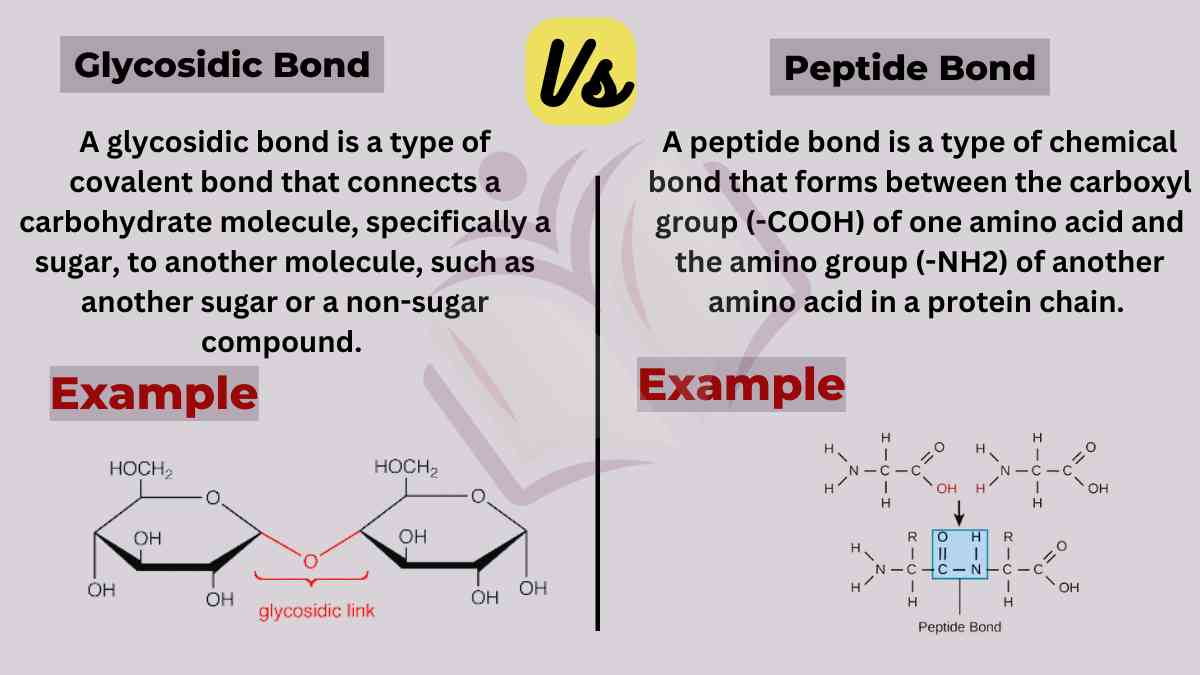
A glycosidic bond is a type of covalent bond that connects a carbohydrate molecule, specifically a sugar, to another molecule, such as another sugar or a non-sugar compound.
It is formed through a condensation reaction between the hydroxyl group (-OH) of one sugar molecule and the anomeric carbon atom (the carbon-containing the carbonyl group) of another sugar molecule or a non-sugar moiety.
What is a peptide bond?
A peptide bond is a type of chemical bond that forms between the carboxyl group (-COOH) of one amino acid and the amino group (-NH2) of another amino acid in a protein chain.
It is formed through a condensation reaction, where a water molecule is eliminated, resulting in the formation of a covalent bond between the carbon atom of the carboxyl group and the nitrogen atom of the amino group.
Glycosidic vs peptide bond
The key difference between a glycosidic bond and a peptide bond is given below:
| Glycosidic Bond | Peptide Bond | |
| Formation | Formed between a carbohydrate and another molecule, typically another carbohydrate or an alcohol. | Formed between two amino acids in a protein. |
| Components | Involves a glycosidic linkage between a sugar molecule and another molecule (e.g., sugar-sugar, sugar-alcohol). | Involves an amide linkage between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid. |
| Reaction | Formation involves the condensation (dehydration) reaction, where a water molecule is eliminated. | Formation involves the condensation (dehydration) reaction, where a water molecule is eliminated. |
| Monomers | Monomers involved are carbohydrates or sugars. | Can be hydrolyzed by adding a water molecule, breaking the bond, and separating the amino acids. |
| Polymers | Glycosidic bonds contribute to the formation of polysaccharides, such as starch and cellulose. | Peptide bonds contribute to the formation of polypeptides and proteins. |
| Hydrolysis | Can be hydrolyzed by adding a water molecule, breaking the bond and separating the monomers. | Examples of peptide bonds include the bonds between amino acids in proteins like enzymes and antibodies. |
| Examples | Examples of Glycosidic bonds include the bonds between glucose molecules in cellulose and sucrose. | Can be hydrolyzed by adding a water molecule, breaking the bond, and separating the monomers. |
