The primary difference between ingestion and egestion is that Ingestion is the process of taking in food or substances into the body, typically through the mouth, to initiate digestion. While Egestion is the elimination of undigested waste materials from the body, usually through the rectum and anus, completing the digestive process.
In this article, we will discuss the difference between ingestion and egestion. We will also give deep insight into separately on both.
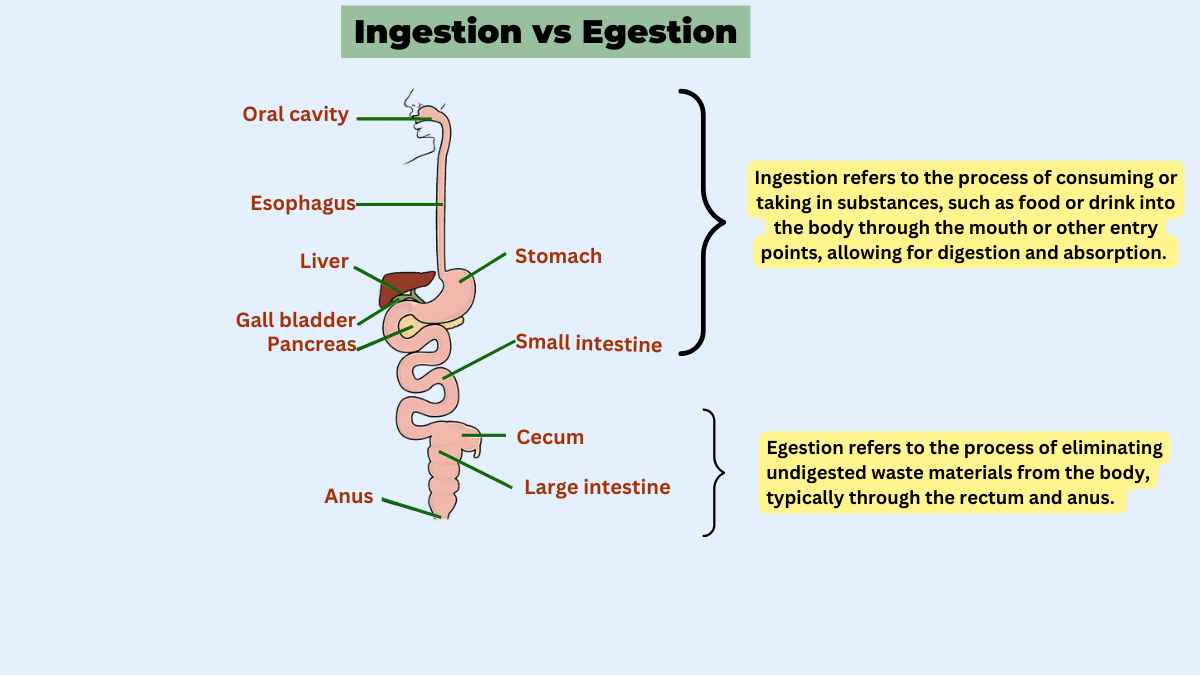
What is Ingestion?
Ingestion refers to the process of consuming or taking substances, such as food, drink, or medication, into the body through the mouth or other entry points, allowing for digestion and absorption. It is a fundamental physiological activity necessary for nourishment, hydration, and the intake of essential nutrients.
What is Egestion?
Egestion refers to the process of eliminating undigested waste materials from the body, typically through the rectum and anus. It is a vital function of the digestive system that ensures the removal of indigestible substances.
Ingestion vs Egestion
The main differences between ingestion and egestion are given below:
| Feature | Ingestion | Egestion |
| Definition | The process of taking in food or other substances into the body through the mouth and esophagus for digestion and absorption. | The process of eliminating or expelling undigested waste material, such as feces, from the body. |
| Occurrence | Occurs in the digestive system. | Occurs mainly in the large intestine and rectum. |
| Function | Prepares food for digestion by breaking it down physically and chemically. | Eliminates waste and toxins from the body. |
| Major Organs | Mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine. | Large intestine (colon), rectum, anus. |
| Mechanism | Food is chewed, mixed with saliva, and swallowed. It then travels through the digestive system for further breakdown and absorption of nutrients. | The process of taking food or other substances into the body through the mouth and esophagus for digestion and absorption. |
| End Product | Partially digested food, nutrients, and water are absorbed into the bloodstream. | Undigested waste material, such as fiber, indigestible matter, and dead cells, is eliminated as feces. |
| Control | Ingestion is primarily under conscious control. | Egestion is largely under involuntary control and regulated by the reflex actions of the gastrointestinal system. |
| Frequency | Occurs whenever food or substances are consumed. | Occurs periodically, depending on the individual’s digestion and bowel movement patterns. |
| Adaptations | Teeth and salivary glands aid in the mechanical breakdown of food. Digestive enzymes facilitate chemical digestion. | The large intestine absorbs water and electrolytes from the waste material, making the feces more solid. The rectum stores feces until it is expelled during defecation. |
| Purpose | Provides the body with energy and essential nutrients for growth, repair, and maintenance. | Removes indigestible waste and helps maintain a healthy balance in the digestive system. |
