The basic difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is that prokaryotes lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotes have a nucleus and various membrane-bound organelles.
In this article, we will discuss the difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. We will also give deep insight into separately on both.
What is a prokaryote?
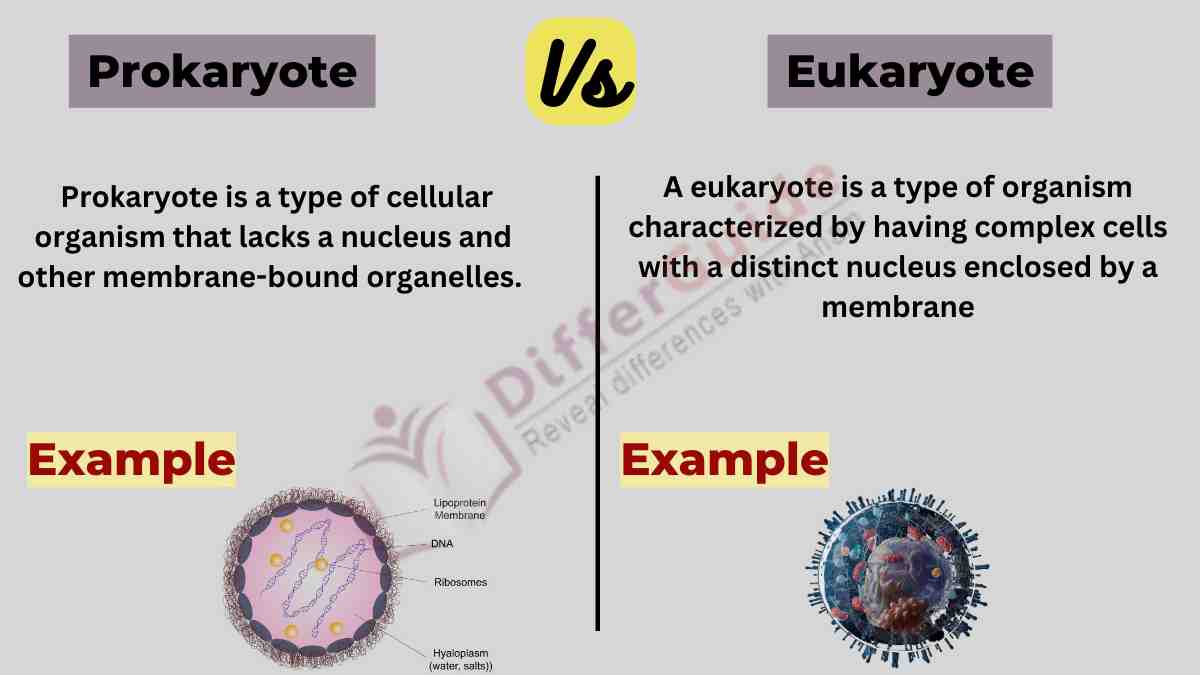
A prokaryote is a type of cellular organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The term “prokaryote” comes from the Greek words “pro” meaning “before” and “karyon” meaning “nucleus.” Prokaryotes are unicellular and are typically smaller and simpler in structure compared to eukaryotic cells.
What is Eukaryote?
Eukaryotes are organisms that have eukaryotic cells, which are characterized by the presence of a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells are more complex compared to prokaryotic cells.
Prokaryote vs Eukaryote
The main difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is given below:
| Characteristic | Prokaryotes | Eukaryotes |
| Nucleus | Absent | Present |
| DNA | Singular, circular, or linear | Multiple, linear, and organized into chromosomes |
| Membrane-bound organelles | Absent | Present (e.g., mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, etc.) |
| Size | Usually smaller (1-10 μm) | Usually larger (10-100 μm) |
| DNA is associated with histones and contains introns | Binary fission | Mitosis (for somatic cells) and meiosis (for reproductive cells) |
| Genetic material | Naked DNA (no histones or introns) | DNA associated with histones and contains introns |
| Examples | Bacteria, archaea | Animals, plants, fungi, protists |
