The primary difference between xylem and phloem is that xylem is composed of dead cells and primarily conducts water upward, while the phloem contains living cells and can transport nutrients bidirectionally.
What is the Xylem?
Xylem is a specialized plant tissue responsible for the transportation of water, minerals, and nutrients from the roots to the rest of the plant.
It consists of specialized cells called tracheids and vessel elements that form long, interconnected tubes. These tubes create a continuous pathway for water movement, enabling efficient upward flow through the plant’s stem and branches.
What is Phloem?
Phloem is another specialized plant tissue that works in conjunction with the xylem to facilitate the transportation of substances throughout the plant.
While the xylem primarily transports water and minerals from the roots upwards, the phloem transports sugars, organic compounds, and other nutrients in both upward and downward directions.
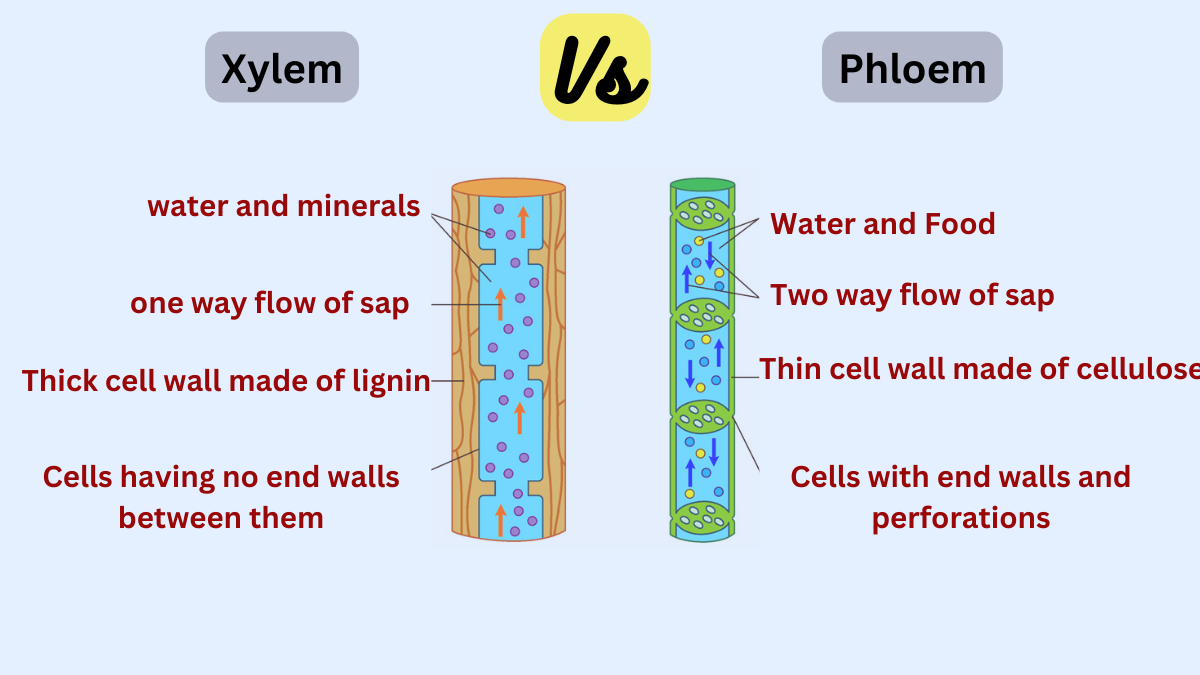
Xylem vs Phloem
The main difference between the xylem and phloem is given below:
| Characteristic | Xylem | Phloem |
| Support | Provides structural support to the plant. | Less involved in structural support. |
| Direction of flow | Unidirectional (upward). | Bidirectional (upward and downward). |
| Contents Transported | Water, minerals, and dissolved nutrients. | Organic compounds, mainly sucrose. |
| Composition | Xylem is composed of several types of cells, including tracheids, vessel elements, fibers, and parenchyma cells. | Phloem consists of four main types of cells: sieve tube elements, companion cells, phloem fibers, and phloem parenchyma. |
| Function | The main function of the xylem is to transport water and minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant. | The main function of the xylem is to transport water and minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant. |
| Location in stem | The outer region of the stem, towards the periphery. | The outer region of the stem, towards the periphery. |
| Cell Structure | No end walls between cells (continuous tubes). | End walls (sieve plates) present between cells. |
